Background
Metastatic colorectal cancer involving mostly the liver (LM-CRC), present in about 50% of patients with CRC, and represents a poor prognostic factor contributing to shorter survival. The treatment of patients with unresectable LM-CRC consists of systemic therapy and local treatment, such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). TACE is used either to downstage the tumour to resectable state, or for disease control, enabling local drug delivery with a minimal systemic toxicity and favourable response.
Objective:
To evaluate pharmacokinetic and safety profile of LifePearl microspheres loaded with irinotecan (LifePearl-IRI) in the treatment of liver-dominant, metastatic colorectal carcinoma (LM-CRC) by transarterial chemoembolization.
Methods
In a prospective, multicentre pharmacokinetic study, 14 patients with LM-CRC progressing on at least one line of chemotherapy were treated with LifePearl-IRI.
Six patients received unilobar treatment, treating one lobe per session with 100 mg of irinotecan every 2 weeks. Eight patients received bilobar treatment, treating two lobes per session with 100 mg of irinotecan each (200 mg in total), every 4 weeks.
The total number of procedures was 36.
Results
Maleux et al study (n=14) demonstrated:
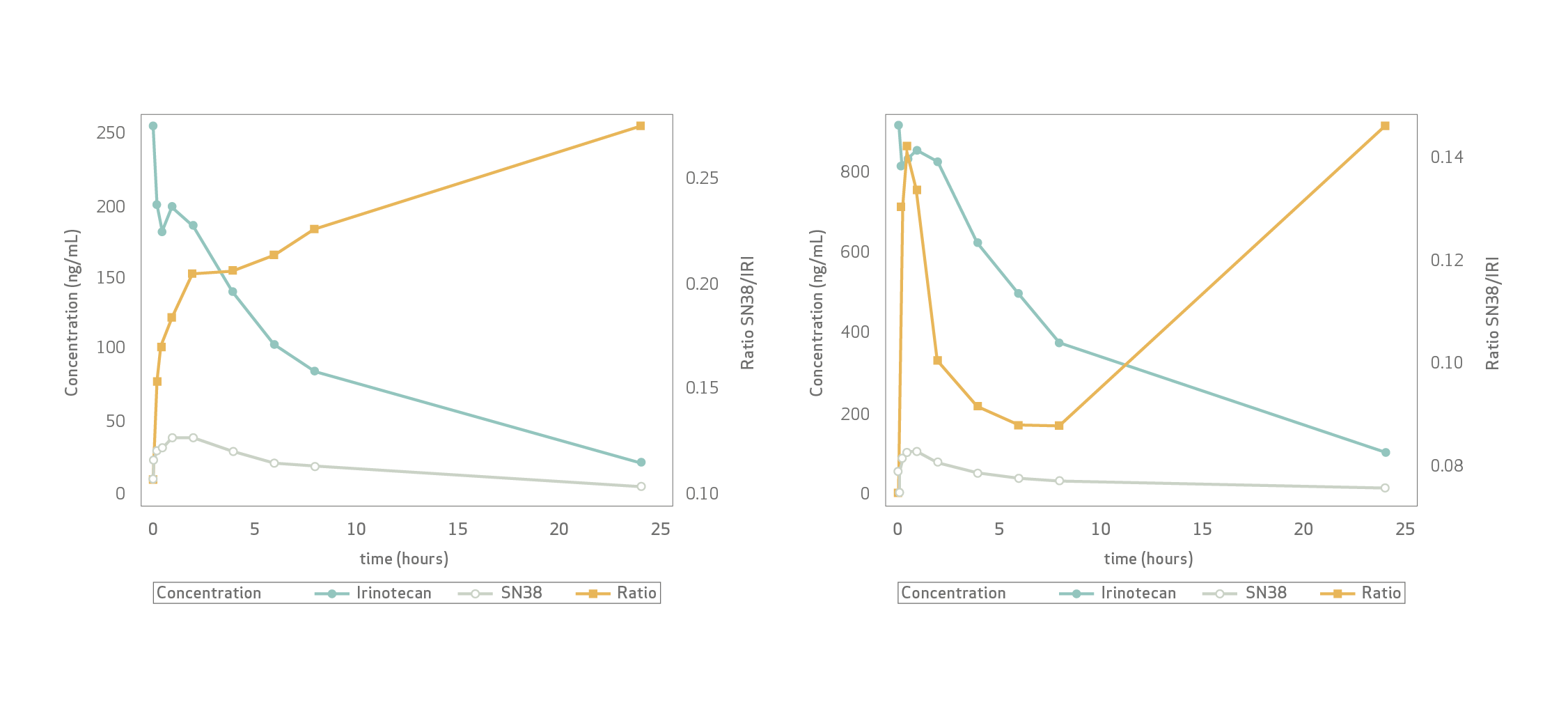
At 24 h, near complete plasma clearance occurred for both irinotecan and SN-38, regardless of the dose.
Mean plasma Cmax (100 mg) was 254.50±104.17 ng/ mL for irinotecan and 46.72±13.75 ng/mL for SN-38.
Mean Cmax (200 mg) was 970.09±353.75 ng/mL for irinotecan and 118.45±25.11 ng/mL for SN-38. Significantly higher Cmax-iri (200 mg) than Cmax-iri (100 mg) supported rate-limiting irinotecan-to-SN-38 conversion.
Adverse events during the first 30 days upon initial treatment were hypertension in 21.4%, abdominal pain in 14.3%, and increased transaminases and fever in 7.1% of patients.
Four serious adverse events were noted: respiratory failure, constipation, necrotizing pancreatitis, and ischaemic cholecystitis.
Limitations: A small number of patients, redefinition of the treatment groups and short follow-up period represent the study limitations. In addition, the comparative analysis of different sizes of drug-eluting beads was not performed. However, this is the first study comparing pharmacokinetic data of a micro-embolic device using 100 and 200 mg of irinotecan per procedure. Such a different dosing and different approach (unilobar vs bilobar) enabled insight into the dynamics of irinotecan metabolism, providing for the first time clinical evidence of rate-limiting irinotecan-to-SN-38 conversion.
Conclusion
Maleux et al concluded that chemoembolization with LifePearl-IRI is technically feasible and relatively well tolerated, with a good pharmacokinetic profile and minimal systemic exposure of both irinotecan and SN-38, after both unilobar and bilobar treatment with 100 or 200 mg of irinotecan respectively.
Key Takeaway:
According to Maleux et al:
Chemoembolization with LifePearl- IRI is technically feasible, with a comparable safety profile to other available micro-embolics, and shows good pharmacokinetic properties after both unilobar and bilobar approaches, with 100 or 200 mg of irinotecan respectively.
Pharmacokinetic data confirm a minimal systemic exposure of both irinotecan and its active metabolite. The study provided for the first time the clinical evidence of rate-limiting irinotecan-to-SN-38 conversion.
Access to full publication: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32932279/
Use/Indications
European Economic Area Indications for use
LifePearl™ microspheres are indicated for embolization of blood vessels supplying primary hypervascular tumours or metastases in the liver. Note: LifePearl™ microspheres can be loaded with chemotherapeutic drugs. When used for drug loading, drug loading should be done under a physician's direction, choice and responsibility, based on type and dose of drug most beneficial to the patient. LifePearl™ microspheres are compatible with doxorubicin, epirubicin idarubicin and irinotecan. LifePearl™ microspheres can be drug loaded prior to embolization and then, as a secondary action, elute a local, controlled, and sustained dose to the targeted tumour sites after embolization. LifePearl™ microspheres are not available for sale in all countries. This information is provided only in respect to markets where this product is approved or cleared.
This literature summary is not a systemic review. It is only an example of LifePearl microspheres related literatures.
The use of the LifePearl™ devices in combination with drugs is not cleared or approved in the USA by the Food and Drug Administration. LifePearl™ microspheres are not approved in Canada. Please consult the indication of use with the IFU supplemented with the product.
Please contact your Terumo local sales representative for more information. All brand names are trademarks or registered trademarks of TERUMO CORPORATION and their respective owners. Refer to Instructions for Use for Contraindications, Warnings and Precautions.
©2020 MicroVention Europe CE0297
Manufacturer
MicroVention Europe
30 bis, rue du Vieil Abreuvoir
78100 Saint-Germain-en-Laye - France
Tel: +33(0)1 39 21 77 46
Distributor
Terumo Europe N.V.
Interleuvenlaan 40
3001 Leuven Belgium
Tel: +32 16 38 12 11
